Noise Characterisation Tutorial
The purpose of this tutorial is to demonstrate the basic workflow of the QREM characterization module.
import numpy as np
from typing import Dict, Tuple, List
from qrem.qtypes.characterization_data import CharacterizationData
from qrem.characterization import characterization
from qrem.common import probability, math as qrem_math
from qrem.cn import simulation as cnsimulation
from qrem.providers import simulation as simulate_experiment
from qrem.common.printer import qprint, qprint_array
from qrem.qtypes import CNModelData
from datetime import date
from typing import Tuple, Dict, List, Optional, Type
from qrem.common.printer import qprint
from qrem.visualisation import benchmark_plots_functions as plot_functions
###List of contents
Analysis of the experimental data
2.1 Initial steps
2.3 Calculation of reduced POVMs and noise matrices
2.4 Calculation of POVM distances
Data generation for characterization routine
This part of code is used to generate data for the characterization workflow. It uses QREM simulator of the readout noise.
number_of_qubits = 10
experiment_type = "DDOT"
number_of_circuits = 200
number_of_shots = 10**4
include_benchmark_circuits = False
number_of_benchmark_circuits = 10
number_of_3_qubit_clusters = 1
number_of_2_qubit_clusters = 3
number_of_1_qubit_clusters = 1
noise_model_simulation=cnsimulation.create_random_noise_model(number_of_qubits=number_of_qubits,clusters_specification=[[3,number_of_3_qubit_clusters], [2, number_of_2_qubit_clusters], [1, number_of_1_qubit_clusters]])
characterization_data_container = CharacterizationData()
characterization_data_container.experiment_type = 'DDOT'
characterization_data_container.results_dictionary = simulate_experiment.simulate_noisy_experiment(noise_model=noise_model_simulation,number_of_circuits=number_of_circuits,number_of_shots=number_of_shots).counts
WARNING: Possible count of random circuits (200) is lower than desired total circuit count (1315).
10
completeness: True
Adding 190 random circuits to a 10-element set
Set of 200 circuits, completeness: True
noisy results generated in: 8.549237251281738 seconds
Characterization Routine
Initial steps
To perform characterization one needs to specify:
qubit_indices - a list of indices of qubits of interest (one might be interested in a subset of all qubits of a device). Here we are interested in all qubits.
marginals_to_compute - a list of tuples encoding qubit marginals for which relevant noise quantifiers are computed. Here the focus is on at most two qubit quantities and the list is as composition of single- and two-qubit marginals.
qubit_indices = [i for i in range(number_of_qubits)]
single_qubit_marginals = [(i,) for i in range(number_of_qubits)]
two_qubit_marginals = [(i, j) for i in range(number_of_qubits) for j in range(i + 1, number_of_qubits)]
marginals_to_compute= single_qubit_marginals + two_qubit_marginals
Marginals coputation
Marginals computation is performed using compute_marginals_single function of probability submodule. One needs to specify:
results_dictionary - dictionary storing experimental results. Here it is characterization_data_container.results_dictionary.
subsets_list - a list of tuples encoding marginals of interest. Here set to marginals_to_compute.
normalization - a bool specifying whether marginals are normalized. Here set to True.
characterization_data_container.marginals_dictionary = probability.compute_marginals_single(results_dictionary=characterization_data_container.results_dictionary,subsets_list=marginals_to_compute,normalization=True)
Computation of reduced POVMs and nosie matrices
Computation of the reduced POVMs and noise matrices is performed using compute_reduced_POVMs_and_noise_matrices. One needs to specify:
characterization_data - results and marginals data stored in an object of the CharacterizationData class, here characterization_data_container
subset_of_qubits - list of marginals of interest, here marginals_to_compute
noise_matrices_dictionary, POVMs_dictionary = characterization.compute_reduced_POVMs_and_noise_matrices(characterization_data=characterization_data_container,subset_of_qubits=marginals_to_compute)
characterization_data_container.POVMs_dictionary = POVMs_dictionary
characterization_data_container.noise_matrices_dictionary = noise_matrices_dictionary
100%|██████████| 55/55 [00:00<00:00, 3993.54it/s]
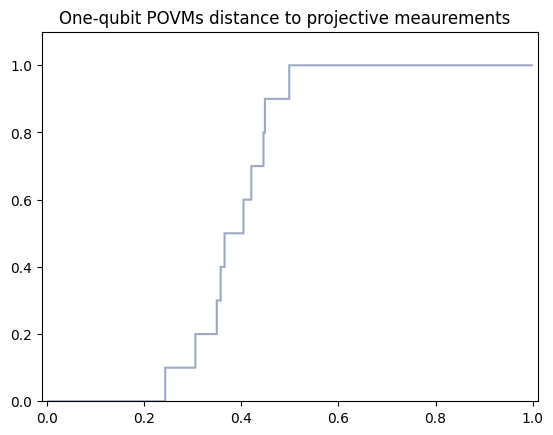
Computation of POVMs errors
Distance computation between ideal projectors in the computational basis and reconstructed noisy reduced POVMs is computed by compute_errors_POVMs function. One needs to specify:
POVMs_dictionary - dictionary with reconstructed POVMs, here characterization_data_container.POVMs_dictionary
qubits_subsets - list of tuples encoding marginals of interest, here set to single_qubit_marginals
distances_types - a list of tuples encoding distances of interest. Possible choices
first position: “worst_case” and “averaged_case”
second position: “classical” and “quantum”
Here set to (‘worst_case’,’classical’)
distances_types = [('worst_case','classical')]
characterization_data_container.POMVs_errors_dictionary = characterization.compute_errors_POVMs(POVMs_dictionary=characterization_data_container.POVMs_dictionary,qubits_subsets=single_qubit_marginals,distances_types=distances_types)
Calculating errors of type: ('worst_case', 'classical')
100%|██████████| 10/10 [00:00<00:00, 12756.40it/s]
DONE
The results can be plotted using built-in visualization function
plot_functions.create_POVMs_distance_histogram(POVMs_errors=characterization_data_container.POMVs_errors_dictionary,number_of_qubits=number_of_qubits)
/home/tuzjan/Documents/QREM_DEVELOPMENT/QREM_SECRET_DEVELOPMENT/venv_jtdev/lib/python3.10/site-packages/matplotlib/axes/_axes.py:6805: RuntimeWarning: invalid value encountered in multiply
tops = (tops * np.diff(bins))[:, slc].cumsum(axis=1)[:, slc]
<Figure size 640x480 with 0 Axes>
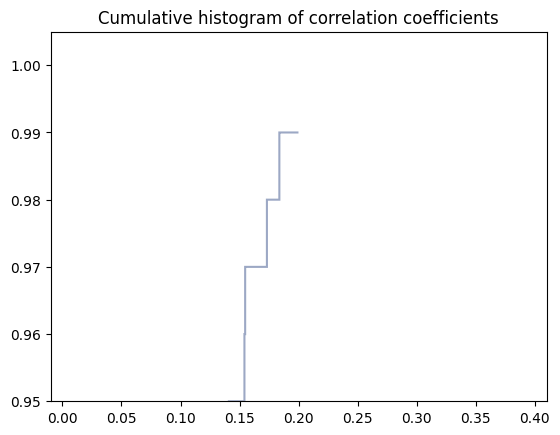
Computation of correlation coefficients
Correlation coefficients, which quantify pairwise correlations in the readout noise, are computed using compute_correlations_data_pairs function. One needs to specify:
qubit_indices - a list of qubits of interest. Here set to qubit_indices, this is all qubits
POVMs_dictionary - dictionary with reconstructed POVMs, here characterization_data_container.POVMs_dictionary
distances_types - a list of tuples encoding distances of interest. Possible choices described above
Here set to (‘worst_case’,’classical’)
characterization_data_container.correlation_coefficients_dictionary = characterization.compute_correlations_data_pairs(qubit_indices=qubit_indices,POVMs_dictionary=characterization_data_container.POVMs_dictionary,distances_types=distances_types)
Calculating correlations of type: ('worst_case', 'classical')
100%|██████████| 45/45 [00:00<00:00, 2477.44it/s]
DONE
The results can be plotted using built-in visualization function
plot_functions.create_correlations_distance_histogram(correlations_coefficients_matrix=characterization_data_container.correlation_coefficients_dictionary[distances_types[0][0]][distances_types[0][1]])
<Figure size 640x480 with 0 Axes>
CN noise models reconstruction
Clustering algorithm is run to reconstruct CN noise models from experimental data. Function perform_clustering_routine returns a list of object, which store all relevant parameters of the reconstructed CN noise models. One needs to specify:
characterization_data - characterization_data - results and marginals data stored in an object of the CharacterizationData class, here characterization_data_container
number_of_qubits - integer encoding number of qubits involved
clustering_functions_parameters - a dictionary specifying parameters of the clustering algorithm with keys:
‘sizes_clusters’ - a list of integers specifying allowed localities of the CN noise models, here set to [2,3,4]
‘distance_type’ and ‘correlations_type’ - string encoding distance type used to compute correlation coefficients, here ‘worst_case’ and ‘classical’
‘alpha_hyperparameters’ - a list of floats encoding parameter entering optimization involved in clustering, here and by default set [0] }
find_neighbors - bool specifying whether neighborhoods of clusters are established, here set to False
clustering_functions_parameters = {'sizes_clusters':[2,3,4],'distance_type':'worst_case','correlations_type': 'classical','alpha_hyperparameters': [0] }
find_neighbors = False
characterization_data_container.clusters_neighbors_sets_dictionary = characterization.perform_clustering_routine(characterization_data = characterization_data_container, number_of_qubits=number_of_qubits,clustering_functions_parameters = clustering_functions_parameters,perform_neighbors_search=find_neighbors)
Current max cluster size: 2
Current max cluster size: 3
Current max cluster size: 4